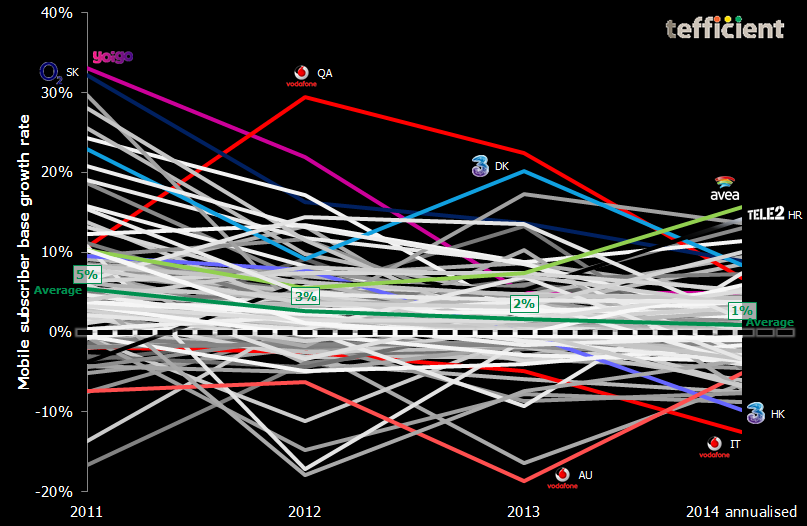
The graph below shows the annual (2014: annualised) growth rate in reported mobile SIM base for about 100 mobile operators in mature markets globally.
Category Archives: Analysis
Copper Europe?
Whereas the “Europe is behind” accusation today is a myth rather than a fact when it comes to 4G LTE rollout, Europe still has an issue when it comes to really fast, two-way, fixed broadband – something only fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) or fiber-to-the-building (FTTB) networks can deliver. Continue reading Copper Europe?
Churn: Still a concern
The subsidy model – which dominated operators’ handset and equipment sales in mature markets for decades – is rightfully retiring. It wasn’t a brilliant idea to discount goods not produced inhouse (taking cost pressure away from equipment manufacturers like Apple) and, to compensate, overcharge for the services actually produced (making over-the-top services and Wi-Fi more attractive). Continue reading Churn: Still a concern
4G LTE coverage: Europe catching up, led by less populated countries
For a long time, lobbyists used the 4G LTE rollout and -adoption discrepancy between US and Korea/Japan (on one hand) and Europe (on the other hand) as a “proof” of too rigid European telecom regulation.
The basic fact that major US, Korean and Japanese operators are running CDMA2000 without the European possibility to gracefully migrate to 4G LTE was tactically neglected in this comparison. Continue reading 4G LTE coverage: Europe catching up, led by less populated countries
“Peak data” in sight
 This is tefficient’s 10th public analysis on the development of mobile data usage. For the first time, we see clear signs of saturation.
This is tefficient’s 10th public analysis on the development of mobile data usage. For the first time, we see clear signs of saturation.
Operators’ squeeze-out of unlimited customers continues. The growth in smartphone penetration has levelled out in high usage markets. 4G is becoming mainstream. Public Wi-Fi starts to disrupt.
Are we approaching “peak data”?
Download analysis: tefficient industry analysis 7 2014 mobile data usage peak ver 2
New operator Wi-Fi analysis: Straight to the top
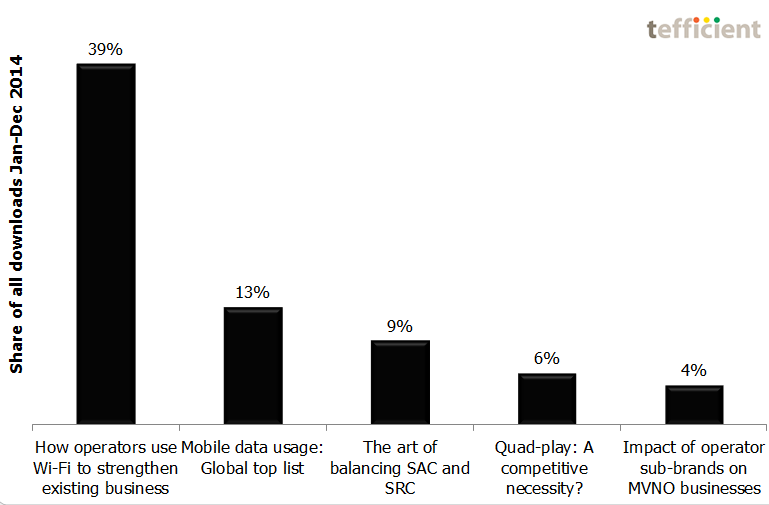
Our new public analysis of How operators use Wi-Fi to strengthen existing business went right into the No 1 position of most downloaded in 2014 – even though it was made available as late as 8 December.
The presentation at the Wi-Fi Innovation Summit seems to have created a lot of interest: The analysis was downloaded 800 times in the two weeks thereafter.
You’ll find the other top 5 analyses – and a few more – at the Analysis page.
Speaker at the Wi-Fi Innovation Summit
Analysis & Consulting, 2014
 Preparing and presenting “How are telcos, cellcos and cablecos using Wi-Fi to strengthen existing business?” for 200 participants at the Wi-Fi Innovation Summit in Copenhagen 9-10 December.
Preparing and presenting “How are telcos, cellcos and cablecos using Wi-Fi to strengthen existing business?” for 200 participants at the Wi-Fi Innovation Summit in Copenhagen 9-10 December.
Some of the presented content is available in this analysis.
How operators use Wi-Fi to strengthen existing business
 Wi-Fi has become a tool in the operator toolbox. In this analysis – our third on the subject – we show how telcos, cellcos and cablecos use Wi-Fi to strengthen existing business. It’s a mixture of hotspots, homespots and new business models.
Wi-Fi has become a tool in the operator toolbox. In this analysis – our third on the subject – we show how telcos, cellcos and cablecos use Wi-Fi to strengthen existing business. It’s a mixture of hotspots, homespots and new business models.
Time is right for operators to include Wi-Fi into a combined connectivity experience for customers – a carrier-grade experience. This analysis contains the best practices and the motivation you need.
Download analysis: tefficient public industry analysis 6 2014 How operators use Wi-Fi to strengthen existing business
Identifying non-traditional initiatives to increase efficiency
Analysis & Consulting, 2014
Independently identifying and presenting customer-specific initiatives to increase efficiency to a key customer operator of a global services provider.
How to improve EBITDA margin from 28% to 43% in 12 months
T-Mobile in the Netherlands continues its rally towards higher EBITDA margin: One year ago, it was 28%. Now it’s 43%. T-Mobile’s reported figures shows just how sensitive sales costs are to the mobile business margin.
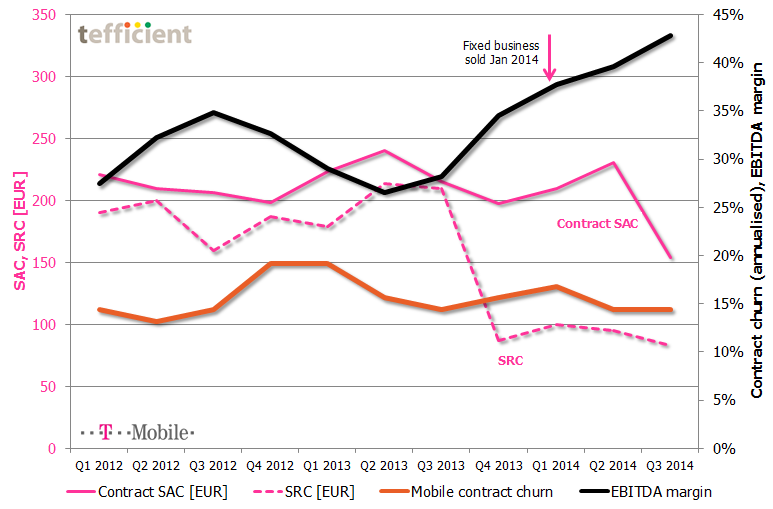
In Q4 2013, T-Mobile cut its subscriber retention cost (SRC) from a level above 200 EUR to less than half. It has stayed at the new, lower, level since. Even though done during fourth quarter – where margin normally is weak due to seasonal sales – T-Mobile’s EBITDA margin took a leap upwards quarter-to-quarter. Another leap came in Q1 2014 when T-Mobile sold its fixed business (traded under the “Online” brand).
In the just-reported third quarter, T-Mobile’s EBITDA margin took yet a leap: This time due to a significant reduction in contract SAC (subscriber acquisition cost).
The text book says that such dramatic reductions in SAC/SRC would immediately penalise T-Mobile who would experience a shrinking base and market share since existing customers would churn out and new customers would’t join. The interesting thing is that existing customers haven’t left: The orange curve shows a stabilising contract churn of about 15%. T-Mobile has, however, still experienced a decline in their total base, but this has mainly been within prepaid. [The reported reduction in Q3 was almost exclusively to the disposal of the Simpel brand].
According to T-Mobile, the answer to how this has been possible comes in two parts:
- Increasing mobile data usage and revenue
- Increasing revenue from equipment
In a market where T-Mobile’s two current MNO competitors KPN and Vodafone both go in the converged multi-play direction, it will be interesting to follow if T-Mobile can stay on this route – especially as Tele2 is about to enter the Dutch market as MNO within short.